Configuring Checks
In Cron HealthChecks service, a Check represents a single service you want to monitor. For example, when monitoring cron jobs, you would create a separate check for each cron job you wish to monitor. Cron HealthChecks service pricing plans are structured primarily around how many checks you can have in your account. You can create checks in the Cron HealthChecks service web interface or via Management API.
Name, Tags, Description
Describe each check using an optional name, slug, tags, and description fields.
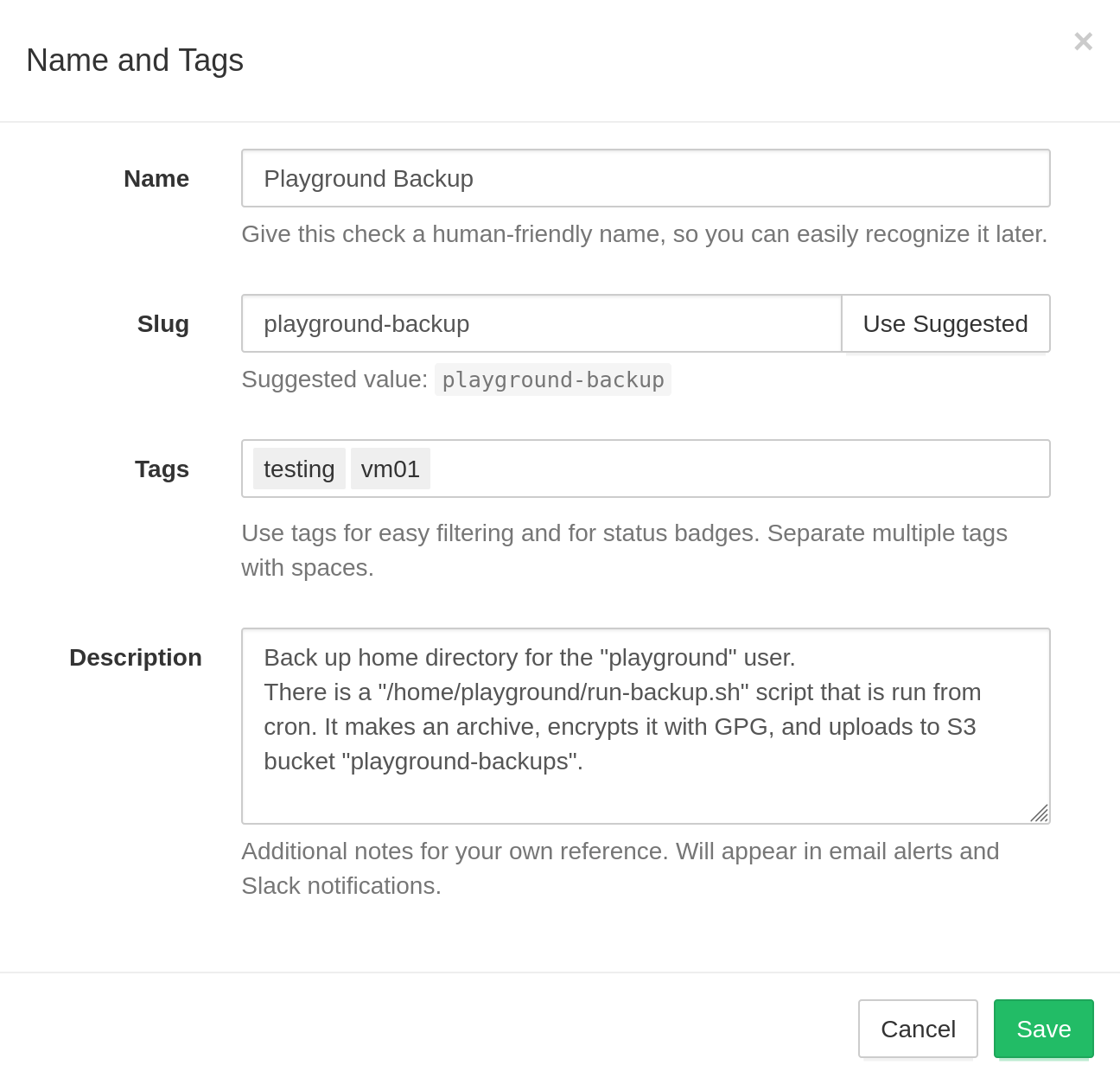
- Name: names are optional, but setting them is a good idea. Good naming becomes especially important as you add more checks to the account. Cron HealthChecks service will display check names in the web interface, email reports, and notifications.
- Slug: URL-friendly identifier used in slug-based ping URLs
(an alternative to the default UUID-based ping URLs). The slug should only contain the
following characters:
a-z,0-9, hyphens, and underscores. If you don't plan to use slug-based ping URLs, you can leave the slug field empty. - Tags: a space-separated list of optional labels. Use tags to organize and group
checks within a project. You can tag checks by the environment
(
prod,staging,dev, etc.), by role (www,db,worker, etc.), or by using any other system. - Description: a free-form text field with any related information for your team or your future self. Describe the cron job's role, who set it up, what to do in case of failures, and where to look for additional information.
Simple Schedules
Cron HealthChecks service supports three types of schedules: Simple, Cron, and OnCalendar. Use Simple schedules for monitoring processes that you expect to run at relatively regular intervals: once an hour, once a day, once a week, etc.
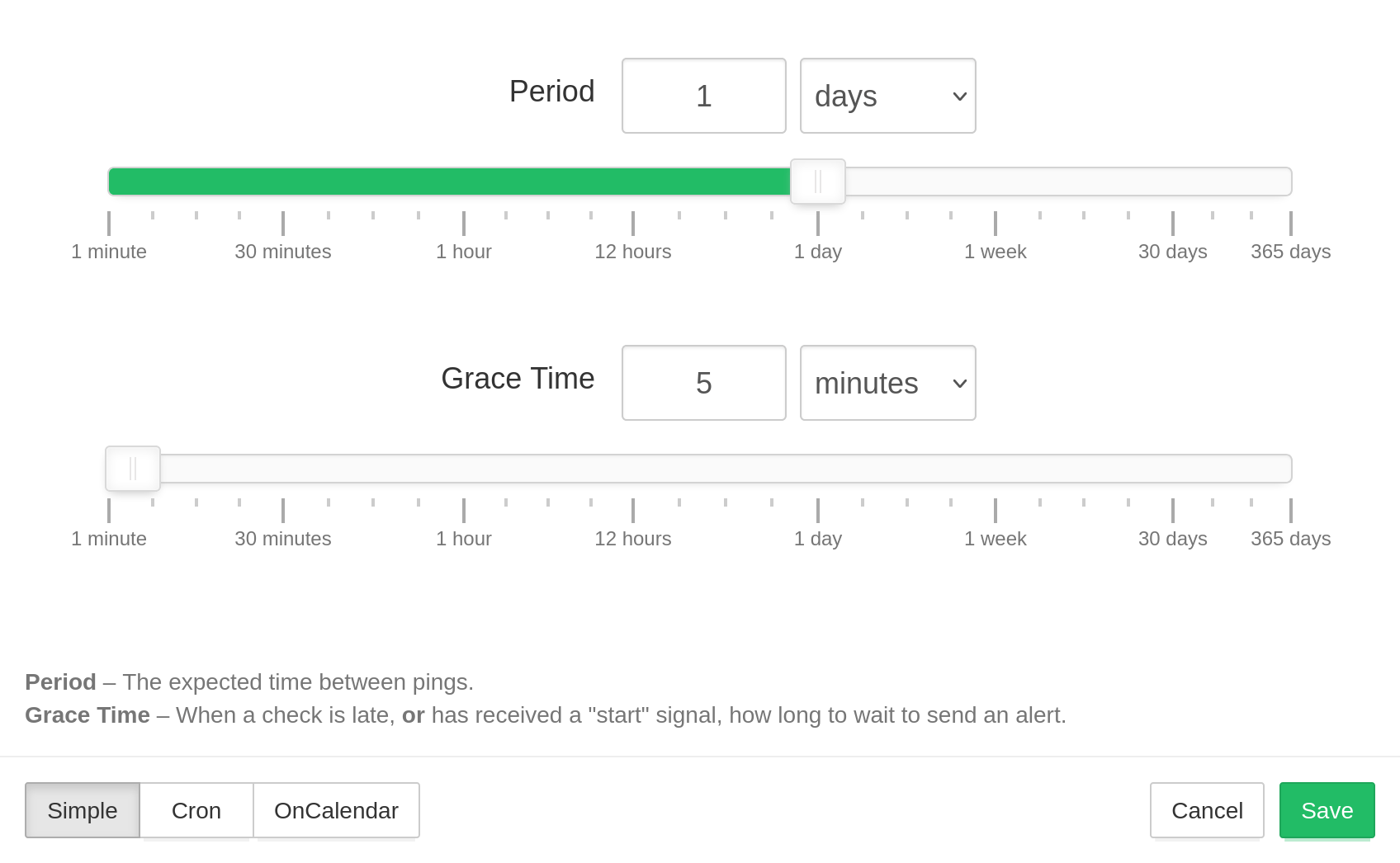
For the simple schedules, you can configure two parameters, Period and Grace Time.
- Period is the expected time between pings.
- Grace Time is the additional time to wait before sending an alert when a check is late. Use this parameter to account for minor, expected deviations in job execution times.
Note: if you use the "start" signal to measure job run times, then Grace Time also specifies the maximum allowed time gap between "start" and "success" signals. Whenever Cron HealthChecks service receives a "start" signal, it expects a subsequent "success" signal within Grace Time. If the success signal does not arrive within the configured Grace Time, Cron HealthChecks service will mark the check as failed and send out alerts.
Cron Schedules
Use "Cron" for monitoring cron jobs and other processes with more complex schedules. This monitoring mode ensures that jobs run at the correct time and not just at the correct time intervals.
See Cron syntax cheatsheet for cron expression syntax examples. See crontab(5) man page for complete cron syntax reference.
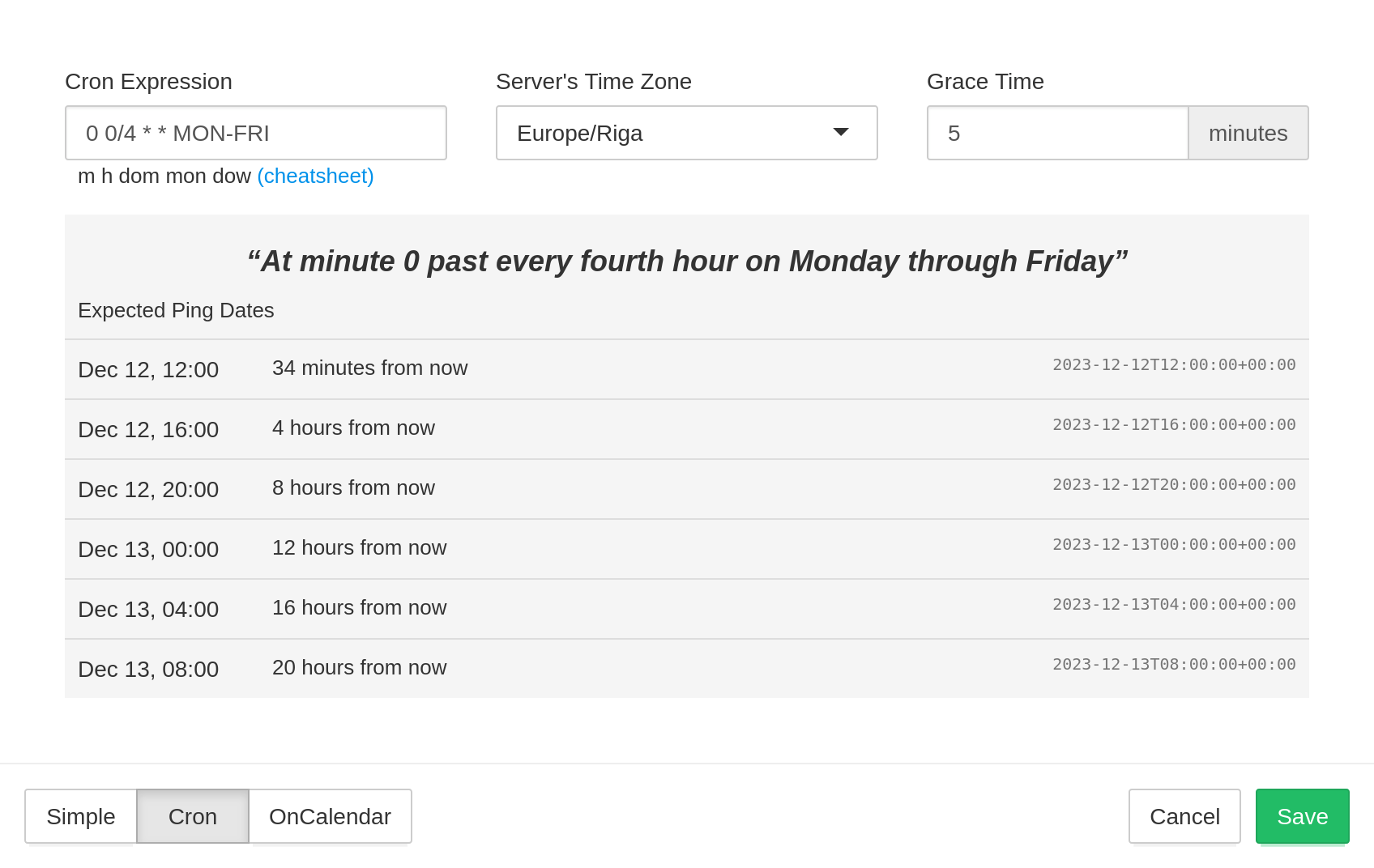
You will need to specify Cron Expression, Server's Time Zone, and Grace Time.
- Cron Expression is the cron expression you specified in the crontab.
- Server's Time Zone is the timezone of your server. The cron daemon typically uses the system's local time. If the machine does not use the UTC timezone, specify its timezone here.
- Grace Time, same as for simple schedules, is how long to wait before sending an alert for a late check.
OnCalendar Schedules
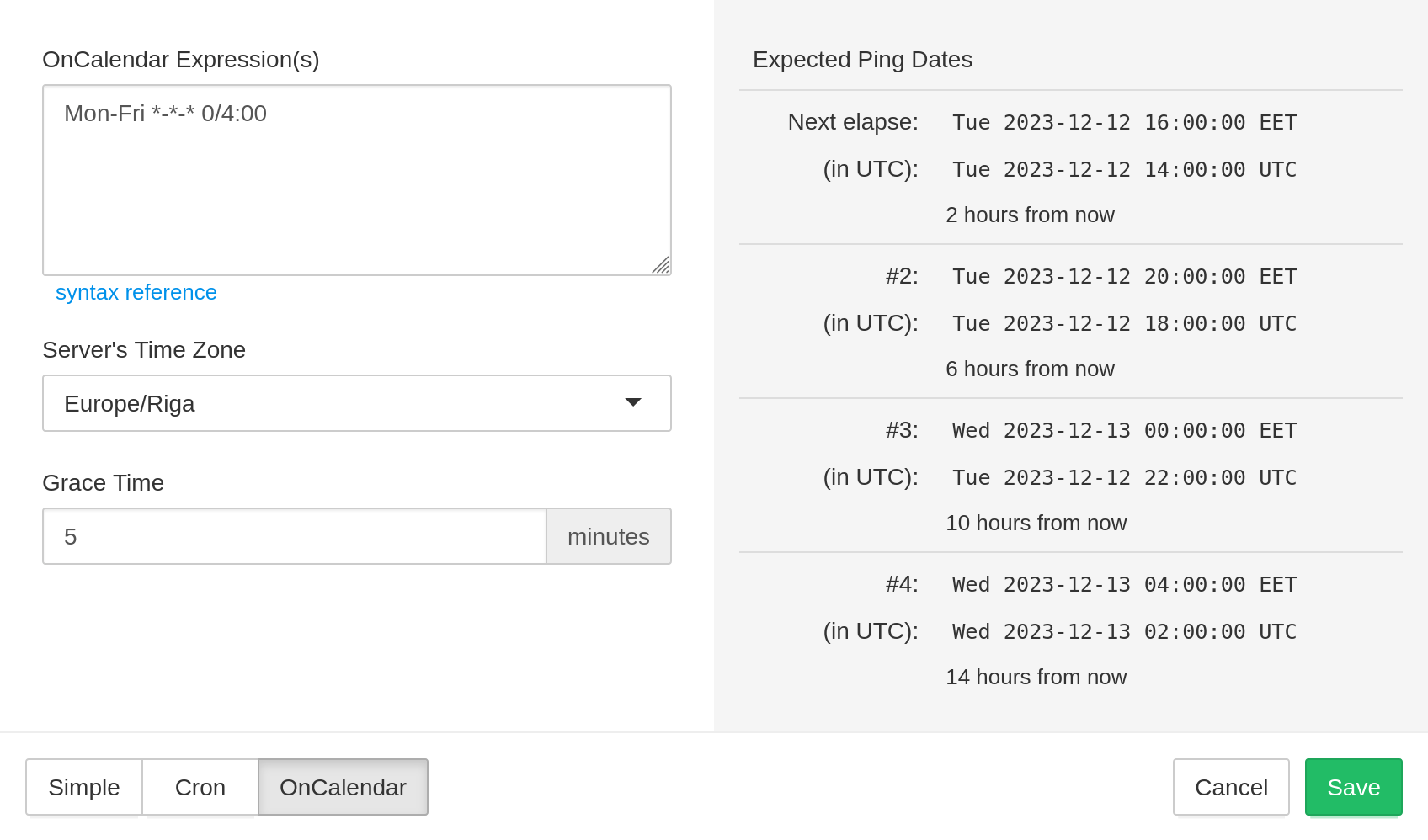
Use "OnCalendar" schedules to monitor systemd timers that use OnCalendar= schedules.
Same as with systemd timers, you can specify more than one OnCalendar expression,
and Cron HealthChecks service will expect a ping whenever any schedule matches.
See systemd.time(7) man page for complete OnCalendar syntax reference.
Filtering Rules
In the "Filtering Rules" dialog, you can control several advanced aspects of how Cron HealthChecks service handles incoming pings for a particular check.

- Allowed request methods for HTTP requests. You can require the ping requests to use HTTP POST. Use the "Only POST" option if you run into issues of preview bots hitting the ping URLs when you send them in email or post them in chat.
- Filter by keywords in the Subject line. When pinging via email,
you can instruct Cron HealthChecks service to look for specific keywords in the subject line. If the
subject line contains any of the keywords listed in Start Keywords,
Success Keywords, or Failure Keywords, Cron HealthChecks service will classify the email as
a start, a success, or a failure signal, respectively. Keyword matching is case-sensitive.
Cron HealthChecks service will first checks for the presence of Failure keywords, then Success
keywords, and then Start keywords. If filtering is enabled but no keywords
match, Cron HealthChecks service will ignore the email message. The email will show in the event log
with an "Ignored" badge.
The keyword filtering feature is useful if, for example, your backup software sends an email after each backup run, but with a different subject line depending on success or failure. - Filter by keywords in the message body. Same as the previous option, but looks for the keywords in the email message body. Cron HealthChecks service checks for keywords both in the plain text and the HTML parts of email messages.
- Pinging a Paused Check. Normally, when you ping a paused check, it leaves the paused state and goes into the "up" state (or the "down" state in case of a failure signal). You can change this behavior by selecting the "Ignore the ping, stay in the paused state" option. With this option selected, the paused state becomes "sticky": Cron HealthChecks service will ignore all incoming pings until you explicitly resume the check.